Understanding Healthy Fats: Good for Your Heart

Understanding the Core Principles
Differentiating between good and bad, or excellent and deficient, is a fundamental aspect of human judgment and decision-making. It requires a clear understanding of the core principles and standards that define the desired outcome. This process often involves critical evaluation and comparison to established benchmarks.
Precisely defining the criteria for good is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable assessments. Without clear standards, judgments become subjective and potentially unreliable.
Evaluating Quality and Performance
Assessing quality and performance involves a multifaceted approach. It often requires considering various factors, including functionality, aesthetics, durability, and user experience. A comprehensive analysis must account for the specific context in which the item or process is being evaluated.
Considering Context and Perspective
The perception of good is significantly influenced by context and perspective. What might be considered good in one situation might not be in another. For example, a solution that works well in a controlled environment may not perform optimally in a dynamic or unpredictable setting.
Acknowledging different viewpoints is essential for a well-rounded evaluation. Considering various perspectives can lead to a more nuanced understanding of the issue at hand.
Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
A critical aspect of differentiation lies in identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the subject under consideration. This involves a thorough examination of the positive attributes and areas needing improvement. A comprehensive analysis of both strengths and weaknesses is crucial for informed decision-making.
Pinpointing these areas helps in focusing on areas for development and improvement, ultimately leading to a better outcome.
Benchmarking Against Established Standards
Benchmarking against established standards or best practices is vital in evaluating quality and performance. This process involves comparing the subject under consideration to industry standards or proven models. This objective comparison allows for identifying areas where the subject excels or falls short.
Using established benchmarks provides a reliable framework for evaluating quality, ensuring that decisions are based on objective criteria rather than subjective opinions.
Applying Relevant Metrics
Applying relevant metrics is a key part of quantifying and analyzing performance. These metrics allow for measurable comparisons and evidence-based conclusions. Using relevant metrics provides a solid foundation for consistent evaluations, leading to more objective judgments.
The selection of appropriate metrics is crucial for ensuring accurate and meaningful assessments. Choosing metrics that align with the goals and objectives is essential for effective evaluations.
Addressing Potential Biases
Recognizing and addressing potential biases is a critical component of objective evaluation. Biases can stem from personal preferences, cultural influences, or pre-existing beliefs. Understanding these biases and actively working to mitigate their impact is crucial for producing reliable results.
Minimizing bias ensures that evaluations are fair, unbiased, and provide an accurate representation of the subject matter. A well-structured evaluation process should explicitly address and mitigate potential biases.
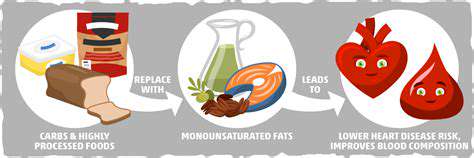
Polyunsaturated Fats: Omega-3s and Omega-6s
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are a crucial type of polyunsaturated fat that our bodies need but cannot produce on their own. They play a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including brain development and function, heart health, and reducing inflammation. Sources of omega-3s include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet can contribute significantly to overall well-being and support a healthy lifestyle.
Research consistently highlights the positive impact of omega-3s on cardiovascular health. These fats help lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and maintain healthy cholesterol levels, all of which contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease. Furthermore, omega-3s are essential for brain function, particularly during development and throughout life, supporting cognitive performance and potentially mitigating the risk of age-related cognitive decline. The potential benefits of omega-3s extend beyond these areas, with ongoing research exploring their role in managing conditions like arthritis and certain mental health disorders.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids: A Balanced Perspective
Omega-6 fatty acids are another essential type of polyunsaturated fat, also crucial for various bodily functions. They are involved in cell growth and development, hormone production, and inflammatory responses. Common sources of omega-6s include vegetable oils like corn oil, soybean oil, and sunflower oil, as well as nuts and seeds. While omega-6s are important, maintaining a balanced intake alongside omega-3s is key for optimal health.
The modern diet often contains a disproportionately high amount of omega-6s compared to omega-3s. This imbalance can contribute to chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues. Understanding the importance of a balanced intake of both omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is critical for overall well-being. By focusing on consuming a variety of foods rich in these fats, while mindful of the overall ratio, individuals can potentially optimize their health and reduce the risk of certain health problems.
It's important to note that while omega-6 fatty acids are necessary, excessive consumption can be problematic. A balanced approach, encompassing a variety of food sources rich in both omega-3s and omega-6s, is vital for maintaining optimal health. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on achieving and maintaining a balanced intake of these essential fatty acids.
Incorporating Healthy Fats into Your Diet: Practical Tips

Choosing the Right Healthy Fats
When incorporating healthy fats into your diet, it's crucial to understand the different types and their respective benefits. Unsaturated fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are essential for various bodily functions, including hormone production and cell growth. These fats are typically liquid at room temperature and are found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Understanding the source of these fats will help you make informed choices about the foods you consume.
Saturated fats, while not inherently harmful in moderation, should be consumed in smaller quantities compared to unsaturated fats. They are solid at room temperature and are primarily found in animal products like meat and dairy. A balanced approach that prioritizes unsaturated fats is key to maintaining a healthy diet.
Benefits of Healthy Fats for Your Body
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet offers a wide range of health benefits. These fats are crucial for brain function and cognitive health, as they're a major component of brain cell membranes. They also play a vital role in nutrient absorption, helping the body effectively process vitamins and minerals from the foods you eat. Furthermore, healthy fats contribute to hormone production, impacting various bodily functions and energy levels.
Furthermore, they can contribute to reducing inflammation in the body, a key factor in preventing chronic diseases and promoting overall well-being. Healthy fats are essential for maintaining healthy skin and hair, impacting their appearance and texture.
Dietary Sources of Healthy Fats
A wide variety of foods provide healthy fats. Avocados, packed with monounsaturated fats, offer a creamy texture and a rich source of essential nutrients. Nuts and seeds, like almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, are excellent sources of both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These provide a satisfying crunch and a concentrated dose of nutrients.
Olive oil, a staple in many cuisines, is renowned for its high monounsaturated fat content. It adds a delicious flavor to dishes and contributes to a healthy diet. Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fat crucial for heart health and overall well-being. A varied diet that includes these foods ensures a diverse intake of healthy fats.
Healthy Fat and Weight Management
Contrary to popular belief, healthy fats can actually support weight management efforts. These fats promote satiety, meaning you feel fuller for longer after a meal. This can help control portion sizes and reduce overall calorie intake. This sustained feeling of fullness can help prevent overeating and contribute to weight loss or maintenance. Furthermore, healthy fats are essential for proper metabolism, which plays a crucial role in how your body processes and utilizes energy.
Including healthy fats in your diet can also help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and cravings that can often lead to unhealthy food choices. By incorporating healthy fats into your meals, you can support a balanced and effective weight management strategy.
Healthy Fat and Heart Health
Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. These fats help reduce inflammation and lower levels of harmful cholesterol. Omega-3s are particularly beneficial for lowering triglycerides, which can contribute to heart disease if left unchecked. Including foods rich in healthy fats in your diet can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Cooking with Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are versatile and can be incorporated into various cooking methods. Olive oil, for example, is excellent for sautéing vegetables, drizzling over salads, and using in baking. Avocado oil is a great alternative, adding a unique flavor profile to dishes. Nuts and seeds can be added to salads, sprinkled on yogurt, or incorporated into homemade granola bars. When using healthy fats for cooking, it's important to choose methods that preserve their nutritional value, such as low-heat cooking. Proper cooking techniques ensure that the beneficial components of these fats remain intact, contributing to their overall health benefits.
Using healthy fats for cooking can elevate the flavor and nutritional content of your meals, promoting a healthier approach to culinary experiences.
- Baking for Beginners: Easy Recipes to Master
- Safely Defrosting Food: Best Practices to Prevent Bacteria
- Discovering Korean BBQ: Essential Marinades and Grilling Tips
- Exploring Middle Eastern Mezze: Hummus, Baba Ghanoush, and More
- Simple Soup Recipes: Warm and Satisfying
- Vegan Lunch Ideas for Work: Easy and Convenient
- Vegetarian Dinner Party Sides: Complement Your Meal
- Baking Gluten Free Brownies: Fudgy and Delicious
- Quick & Easy Chicken Noodle Soup: Comfort Food
- Cooking with Electric Skillet: Versatile Cooking
- Exploring Russian Teacakes: Sweet and Delicate
- Paleo Breakfast Ideas: Grain Free and Satisfying